Category: Linux
SMTP auth relay with postfix
In case that your SMTP server has authentication (like Gmail), For this purpose we will use Postfix. I
Install the needed packages:
Ubuntu
apt-get install postfix mailutils libsasl2-2 ca-certificates libsasl2-modules
CentOS
yum update && yum install postfix mailx cyrus-sasl cyrus-sasl-plain
- Set Postfix config file /etc/postfix/main.cf. Add this lines to the end of the file:
-
Set Postfix config file
/etc/postfix/main.cf. Add this lines to the end of the file:Ubuntu
relayhost = [smtp.gmail.com]:587 smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd smtp_sasl_security_options = noanonymous smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/thawte_Primary_Root_CA.pem smtp_use_tls = yes
CentOS
relayhost = [smtp.gmail.com]:587 smtp_sasl_auth_enable = yes smtp_sasl_password_maps = hash:/etc/postfix/sasl_passwd smtp_sasl_security_options = noanonymous smtp_tls_CAfile = /etc/ssl/certs/ca-bundle.crt smtp_use_tls = yes
-
Configure email address and password:
echo [smtp.gmail.com]:587 USERNAME@gmail.com:PASSWORD > /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd postmap /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd chmod 400 /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd
-
Secure DB password
chown root:root /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd.db chmod 0600 /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd /etc/postfix/sasl_passwd.db
-
Reload Postfix
systemctl reload postfix
-
Test you configuration with:
echo "Test mail from postfix" | mail -s "Test Postfix" you@example.com echo "Test mail from postfix" | mail -s "Test Postfix" -r someone@whatever.com you@example.com (this is if your reply address has to come from a specific sender)
You should receive an email on
you@example.com
You should receive an email on you@example.com
Note: If you are using centos 7, which uses systemD. You will find that postfix doesn’t send maillogs to /var/log/maillog. Someone decided it would be a great idea to send it to the journaler instead.
In order to find your mail logs and or tail the logs for postfix.
- Journalctl -u postfix (view all logs)
- Journalctl -u postfix -f (to tail the mail logs)
How to properly upgrade wazuh with a major update (standalone setup)
Upgrade from the same major version (3.x)
The following steps show how to upgrade to the latest available version of Wazuh 3.x (which implies upgrading to the latest version of Elastic Stack 6.x).
Starting the upgrade
If you followed our manager or agents installation guides, probably you disabled the repository in order to avoid undesired upgrades. It’s necessary to enable them again to get the last packages.
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
#sed –i“s/^enabled=0/enabled=1/” /etc/yum.repos.d/wazuh.repo
Upgrade the Wazuh manager
Note
Since Wazuh v3.7.0 the File Integrity Monitoring database is not used anymore. In order to add to Wazuh DB the file and registry entries stored from previous versions it’s necessary to run the FIM migration tool.
- Upgrade the wazuh-manager package:
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# yum upgrade wazuh-manager
- Upgrade the wazuh-api package:
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# yum upgrade wazuh-api
Note
The installation of the updated packages will automatically restart the services for the Wazuh manager, API and agents. Your Wazuh config file will keep unmodified, so you’ll need to manually add the settings for the new capabilities. Check the User Manual for more information.
Finishing the Wazuh upgrade
You’ve finished upgrading your Wazuh installation to the latest version. Now you can disable again the Wazuh repositories in order to avoid undesired upgrades and compatibility issues.
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
#sed –i“s/^enabled=1/enabled=0/” /etc/yum.repos.d/wazuh.repo
Upgrade to the latest Elastic Stack version
Since the release of Wazuh 3.0.0, there’s been several updates to the 6.x version of the Elastic Stack, introducing several bugfixes and important changes. In order to use the latest version of Wazuh, it’s necessary to install the latest compatible Elastic Stack packages.
- Stop the services:
#systemctl stop filebeat (This you do not need to stop in a standalone setup, because it should not be installed. Filebeat is only used when you have a clustered setup. It sends logs back to the manager when clustered)
#systemctl stop logstash
#systemctl stop kibana
#systemctl stop elasticsearch
- Enable the Elastic repository:
If you followed our Elastic Stack Installation Guide, probably you disabled the repository in order to avoid undesired upgrades for the Elastic Stack. It’s necessary to enable them again to get the last packages.
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
#sed –i“s/^enabled=0/enabled=1/” /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo
Upgrade Elasticsearch
- Upgrade the elasticsearch package:
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# yum install elasticsearch-6.5.1
- Start the Elasticsearch service:
#systemctl daemon-reload
#systemctlenableelasticsearch.service
#systemctl start elasticsearch.service
It’s important to wait until the Elasticsearch server finishes starting. Check the current status with the following command, which should give you a response like the shown below:
# curl "http://localhost:9200/?pretty" { "name" : "Zr2Shu_", "cluster_name" : "elasticsearch", "cluster_uuid" : "M-W_RznZRA-CXykh_oJsCQ", "version" : { "number" : "6.5.1", "build_flavor" : "default", "build_type" : "rpm", "build_hash" : "053779d", "build_date" : "2018-07-20T05:20:23.451332Z", "build_snapshot" : false, "lucene_version" : "7.3.1", "minimum_wire_compatibility_version" : "5.6.0", "minimum_index_compatibility_version" : "5.0.0" }, "tagline" : "You Know, for Search" }
Updating the Elasticsearch template to the latest version is mandatory in order to avoid compatibility issues with the latest versions of Wazuh and the Elastic Stack.
# curl https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh/3.7/extensions/elasticsearch/wazuh-elastic6-template-alerts.json | curl -X PUT "http://localhost:9200/_template/wazuh" -H 'Content-Type: application/json' -d @-
Upgrade Logstash
- Upgrade the logstash package:
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# yum install logstash-6.5.1
- Download and set the Wazuh configuration for Logstash:
- Local configuration:
# cp /etc/logstash/conf.d/01-wazuh.conf /backup_directory/01-wazuh.conf.bak # curl -so /etc/logstash/conf.d/01-wazuh.conf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh/3.7/extensions/logstash/01-wazuh-local.conf # usermod -a -G ossec logstash
- Remote configuration: (We are not using this in our standalone setup and therefore do not need to run this)
# cp /etc/logstash/conf.d/01-wazuh.conf /backup_directory/01-wazuh.conf.bak # curl -so /etc/logstash/conf.d/01-wazuh.conf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh/3.7/extensions/logstash/01-wazuh-remote.conf
- Start the Logstash service:
#systemctl daemon-reload
#systemctlenablelogstash.service
#systemctl start logstash.service
Note
The Logstash configuration file has been replaced for an updated one. If you already configured the encryption between Filebeat and Logstash, don’t forget to check again Setting up SSL for Filebeat and Logstash if you’re using a distributed architecture.
Upgrade Kibana
- Upgrade the kibana package:
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# yum install kibana-6.5.1
- Uninstall the Wazuh app from Kibana:
- Update file permissions. This will avoid several errors prior to updating the app:
#chown -R kibana:kibana /usr/share/kibana/optimize
#chown -R kibana:kibana /usr/share/kibana/plugins
- Remove the Wazuh app:
#sudo -u kibana /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-plugin remove wazuh
- Upgrade the Wazuh app:
# rm -rf /usr/share/kibana/optimize/bundles
#sudo -u kibanaNODE_OPTIONS=“–max-old-space-size=3072” /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana-plugin install https://packages.wazuh.com/wazuhapp/wazuhapp-3.7.1_6.5.1.zip
Warning
The Wazuh app installation process may take several minutes. Please wait patiently.
- Start the Kibana service:
#systemctl daemon-reload
#systemctlenablekibana.service
#systemctl start kibana.service
This section only applies if you have clustered/distributed setup
Upgrade Filebeat
- Upgrade the filebeat package:
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
# yum install filebeat-6.5.1
- Start the Filebeat service:
#systemctl daemon-reload
#systemctlenablefilebeat.service
#systemctl start filebeat.service
Finishing the Elastic Stack upgrade
You’ve finished upgrading your Wazuh installation to the latest version. Now you can disable again the Elastic Stack repositories in order to avoid undesired upgrades and compatibility issues with the Wazuh app.
- For CentOS/RHEL/Fedora:
#sed –i“s/^enabled=1/enabled=0/” /etc/yum.repos.d/elastic.repo
Things you will need to fix after the upgrade
1. Running migration tool for versions before 3.7 for that have upgraded recently:
-
If you upgraded from wazuh 3.6 or newer you will need to run the following migration tool, which migrate the database into a new format for wazuh 3.7When they first introduced the tool it had some fail to exit code if it couldn’t decode a line and it would halt the migration. They have since fixed that, however it look something like this.2018-11-12 15:45:38 [INFO] [32/239] Added 3339 file entries in agent ‘033’ database.
2018-11-12 15:45:38 [INFO] Setting FIM database for agent ‘033’ as completed…
2018-11-12 15:45:38 [INFO] [33/239] Upgrading FIM database for agent ‘034’…
2018-11-12 15:45:38 [INFO] [33/239] Added 61 file entries in agent ‘034’ database.
2018-11-12 15:45:38 [INFO] [33/239] Upgrading FIM database (syscheck-registry) for agent ‘034’…
2018-11-12 15:45:38 [ERROR] Couldn’t decode line at syscheck database.
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “./fim_migrate“, line 320, in <module>
if not check_file_entry(agt[0], decoded[2], s):
File “./fim_migrate“, line 91, in check_file_entry
msg = msg + cfile + b”‘;”
TypeError: cannot concatenate ‘str’ and ‘NoneType‘ objects
working migration tool below
https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh/3.7/tools/migration/fim_migrate.py
2. error “api version type mismatch 3.6.1′‘ :
-
After the upgrade when you go into the kibana interface and it does a systems check you might see this error.
Resolution :
- First make sure all the app versions match.
https://documentation.wazuh.com/current/installation-guide/compatibility_matrix/index.html#api-and-kibana-app
- Next run this on the server side to confirm they match
- cat /usr/share/kibana/plugins/wazuh/package.json | grep –i -E “version|revision“
“version”: “3.7.0”,
“revision”: “0413”,
“version”: “6.4.3”
If all those match then you simply need to do the following to fix it.
- Delete the .wazuh-version index:
curl -XDELETE http://elastic_ip:9200/.wazuh-version
- Restart Kibana:
systemctl restart kibana
Wait for about 30 s – 1 min and now open a new window in your browser, then you should navigate without any more troubles regarding the version mismatching.
Notes: The Wazuh app creates that index when you restart Kibana if it’s not present. If your standalone setup is using localhost then the curl command should be localhost and not the elastic ip.
3. Items listed per screen when listing agents will default back to 17 items for screen and is extremely annoying. You will need to fix this in the following manner.:
# systemctl stop kibana
Let’s open the file under /usr/share/kibana/plugins/wazuh/public/templates/agents-prev/agents-prev.html and look for lines 103-109:
<wz-table flex path=“‘/agents'” keys=“[‘id’,{value:’name’,size:2},’ip’,’status’,’group’,’os.name‘,’os.version’,’version’]” allow-click=“true” row-sizes=“[17,15,13]”></wz-table>
The wz-table tag is related to a Wazuh custom directive which has parameters to easy change that limit.
Replace [17,15,13] by your desired size [50,50,50], where each value refers to different screen sizes. Use 50 for all screen sizes,
and you’ll see 50 agents per page regardless your screen size. Use your desired value, it can be 100 or 150…
My suggestion is to don’t increase more than 50 (Angular performance reasons).
Once you are done save and close the file. Now remove old bundles and check the permissions again:
rm –rf /usr/share/kibana/optimize/bundleschown –R kibana:kibana /usr/share/kibana/optimizechown –R kibana:kibana /usr/share/kibana/plugins
Restart Kibana:
# systemctl restart kibana
It takes a few of minutes until it’s completed, you can check the status using the next command:
# systemctl status kibana -l
You’ll see “Optimizing…”, once you see “App ready to be used” you can remove cache/cookies from your browser and type your App address for accessing it.
4. Errors in wazuh log after upgrade [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”}:
- If you see the following your wazuh.log
- tail -n500 /usr/share/kibana/optimize/wazuh-logs/wazuhapp.log
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.613Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Checking if wazuh-monitoring pattern exists…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.625Z”,”level”:”error”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”[cluster_block_exception] blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.632Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Updating known fields for wazuh-monitoring pattern…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.646Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Didn’t find wazuh-monitoring pattern for Kibana v6.x. Proceeding to create it…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.650Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createWazuhMonitoring]”,”message”:”No need to delete old wazuh-monitoring pattern.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.650Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][configureKibana]”,”message”:”Creating index pattern: wazuh-monitoring-3.x-*”}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.658Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkAPIEntriesExtensions]”,”message”:”Successfully updated API entry extensions with ID: 1535484412304″}
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:24:15.660Z”,”level”:”error”,”location”:”[monitoring][configureKibana]”,”message”:”[cluster_block_exception] blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”
-
- This usually means that one of your partitions is near full and wazuh goes into read only mode because of this, super annoying…..
To fix this you must :
-
- first add diskspace to your lvm, if you don’t know how to do this look it up…haha 😛
- The you must go into the kibana interface and under under dev tools run the following
- PUT wazuh–monitoring-*/_settings{ “index”: { “blocks”: { “read_only_allow_delete“: “false” } }}
-
- Make sure to restart kibana:
- systemctl restart kibana
Once kibana is restarted the log should look show something like this.
- tail -n500 /usr/share/kibana/optimize/wazuh-logs/wazuhapp.log
{“date”:”2018-11-23T00:00:02.464Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
Note: Initially you might only see on entry for that day, however after a few days the logs will look like this.
{“date”:”2018-11-22T14:25:09.166Z”,”level”:”error”,”location”:”[monitoring][configureKibana]”,”message”:”[cluster_block_exception] blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”}
{“date”:”2018-11-23T00:00:02.464Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-24T00:00:01.894Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-25T00:00:02.055Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-26T00:00:01.983Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-27T00:00:02.785Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-28T00:00:02.458Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T00:00:02.163Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:46.871Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize]”,”message”:”Kibana index: .kibana“}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:46.874Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize]”,”message”:”App revision: 0413″}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:46.874Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][configuration]”,”message”:”wazuh.monitoring.enabled: true”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:46.874Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][configuration]”,”message”:”wazuh.monitoring.frequency: 3600 (0 */60 * * * *) “}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:46.874Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][checkKibanaStatus]”,”message”:”Waiting for Kibana and Elasticsearch servers to be ready…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.241Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkWazuhIndex]”,”message”:”Checking .wazuh index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.241Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkWazuhVersionIndex]”,”message”:”Checking .wazuh-version index.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.246Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Creating/Updating wazuh-agent template…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.246Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][checkTemplate]”,”message”:”Updating wazuh-monitoring template…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.945Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”x-pack enabled: no”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.999Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”Found 2 index patterns”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.999Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”Found 1 valid index patterns for Wazuh alerts”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.999Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”Default index pattern found”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:48.999Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”Refreshing known fields for \”index-pattern:wazuh-alerts-3.x-*\””}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.092Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkKnownFields]”,”message”:”App ready to be used.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.181Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkAPIEntriesExtensions]”,”message”:”Checking extensions consistency for all API entries”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.188Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[initialize][checkAPIEntriesExtensions]”,”message”:”Successfully updated API entry extensions with ID: 1535484412304″}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.266Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Creating today index…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.295Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Checking if wazuh-monitoring pattern exists…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.314Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Updating known fields for wazuh-monitoring pattern…”}
{“date”:”2018-11-29T14:41:49.320Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][init]”,”message”:”Skipping wazuh-monitoring pattern creation. Already exists.”}
{“date”:”2018-11-30T00:00:01.567Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-12-01T00:00:02.368Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-12-02T00:00:01.297Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-12-03T00:00:02.052Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-12-04T00:00:01.602Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-12-05T00:00:01.886Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
{“date”:”2018-12-06T00:00:02.870Z”,”level”:”info”,”location”:”[monitoring][createIndex]”,”message”:”Successfully created today index.”}
5. Setup DiskSpaceWatch Cron:
-
- I was getting annoyed with having to deal with the diskspace issues which leads to loss of logs and therefore setup a little bash script called “/usr/bin/diskspacewatch”The script runs as root cron every 30 mins, to get to the cron type ‘crontab -e’
#!/bin/sh
df -h | grep –vE ‘^Filesystem|tmpfs|cdrom‘ | awk‘{ print $5 ” ” $1 }’ | while read output;
do
echo $output
usep=$(echo $output | awk‘{ print $1}’ | cut -d’%’ -f1 )
partition=$(echo $output | awk‘{ print $2 }’ )
if [ $usep –ge75 ]; then
echo “Running out of space!! on wazuh production server. Add space or wazuh will go into read only mode. \”$partition ($usep%)\” on $(hostname) as on $(date)” |
mail -s “Alert: Almost out of disk space, add diskspace to wazuhprod server. $usep%” nick@nicktailor.com
fi
done
-
- If any of the partitions reach 75 percent it will send out an email alert to nick@nicktailor.com
- This is to help avoid log loss from wazuh going into read only mode because of diskspace.
-
- Upgrading wazuh agents to 3.7
Note: Lastly They say in wazuh documentation that the agent is backwards compatible however this is not true in my opinion. Reason being features stop working and now require you to update all the agents. This is not a simple as simply updating the agent….
-
- If you attempt to update the agent simply by yum or apt. It will result in the agent loosing the manager ip and key created.
- This particular piece of the upgrade is something that you should test in a test environment by cloning your entire system to a dev one and running simulations. I learned this the hard way and how to be inventive to get it working.
-
- There is an agent_upgrade tool they provide which is supposed to download the new agent, install, and recopy the manager ip and key to the agent all in one go
-
- List out the agents that need to be upgraded
- /var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade -l
Example.
Example.
waz01 ~]# /var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade -l
ID Name Version
003 centosnewtemp Wazuh v3.6.0
165 test1 Wazuh v3.6.1
192 test2 Wazuh v3.6.1
271 test3 Wazuh v3.3.1
277 test4 Wazuh v3.3.1
280 test5 Wazuh v3.3.1
306 test6 Wazuh v3.3.1
313 test6 Wazuh v3.3.1
-
- Manual update of agent(Successful)
# /var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade -d -a 003
Manager version: v3.7.0
Agent version: v3.3.1
Agent new version: v3.7.0
WPK file already downloaded: /var/ossec/var/upgrade/wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk – SHA1SUM: 79678fd4ab800879aacd4451a64e799c62688b64
Upgrade PKG: wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk (2108 KB)
MSG SENT: 271 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: ok
MSG SENT: 271 com lock_restart -1
RESPONSE: ok
Chunk size: 512 bytes
Sending: /var/ossec/var/upgrade/wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
MSG SENT: 271 com close wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: ok
MSG SENT: 271 com sha1 wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: ok 79678fd4ab800879aacd4451a64e799c62688b64
WPK file sent
MSG SENT: 271 com upgrade wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk upgrade.bat
RESPONSE: ok 0
Upgrade procedure started
MSG SENT: 271 com upgrade_result
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 271 com upgrade_result
RESPONSE: err Cannot read upgrade_result file.
MSG SENT: 271 com upgrade_result
RESPONSE: ok 0
Agent upgraded successfully
-
- Using the list provided by agent_upgrade you can copy the agent id’s to a txt file like
- vi agentupgrade.txt
003
165
192
271
Etc…
-
- You can then use a for loop like so to cycle through the list
-
- for name in `cat agentupgrade.txt`; do /var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade -a $name; echo $name; done
Notes: Exiting the script once its running as it may cause issues as I didn’t put in any error fail to exit obviously.. The other issue I did notice that windows 2016 and windows 7 machines had issues updating the agent I saw the following errors as indicated below. This would update the agent, and then timeout without reinputting the manager ip and key. I had to manually update the failed machines as Wazuh was unable to provide me with answer as to why it was failing. I was able to replicate the issue on 50 machines. So in short if your going to upgrade and have 1000 machines. I highly recommend doing lots of simulations before you upgrade as this is one the most important parts of the upgrade. If they fail to mention in their documentation.
Errors:
# /var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade -d -a 298
Manager version: v3.7.0
Agent version: v3.3.1
Agent new version: v3.7.0
WPK file already downloaded: /var/ossec/var/upgrade/wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk – SHA1SUM: 79678fd4ab800879aacd4451a64e799c62688b64
Upgrade PKG: wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk (2108 KB)
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
MSG SENT: 298 com open wb wazuh_agent_v3.7.0_windows.wpk
RESPONSE: err Maximum attempts exceeded
Error 1715: Error sending WPK file: Maximum attempts exceeded
Traceback (most recent call last):
File “/var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade”, line 165, in <module>
main()
File “/var/ossec/bin/agent_upgrade”, line 119, in main
rl_timeout=-1 if args.timeout == None else args.timeout, use_http=use_http)
File “/var/ossec/bin/../framework/wazuh/agent.py”, line 2206, in upgrade
show_progress=show_progress, chunk_size=chunk_size, rl_timeout=rl_timeout, use_http=use_http)
File “/var/ossec/bin/../framework/wazuh/agent.py”, line 2102, in _send_wpk_file
raise WazuhException(1715, data.replace(“err “,””))
wazuh.exception.WazuhException: Error 1715 – Error sending WPK file: Maximum attempts exceeded
How to survive a log flood – wazuh
This is directly from wazuh documentation, but I thought it would good to have here for people browsing through. I guess the main section to take notice of is how to augment the agent buffer via the ossec.conf on the client side for troubleshooting purposes
Survive a log flood
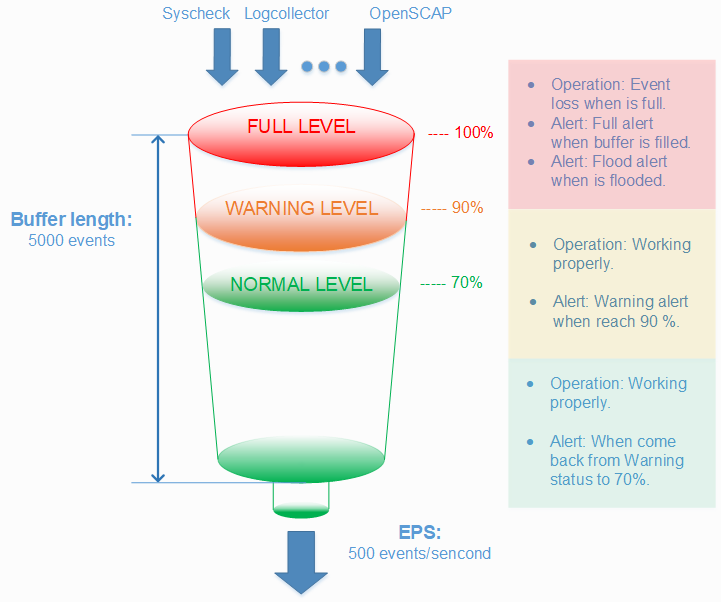
A centralized logging system needs to be able to process many events per second (eps) from many different log sources at the same time, but sometimes things just get completely out of hand. A variety of problems like infinite loop conditions, poorly written software, and misconfigured applications can cause one or a few individual devices to suddenly start producing a huge and unstopping stream of log messages rushing at your logging system at a rate of hundreds or even thousands of events per second. When such a device or devices suddenly take up vastly more than their fair share of network and log processing resources, it can become widely disruptive. Log flooding can saturate your network bandwidth and/or overtax your Wazuh and Elastic system components while one gigabyte after another of likely the same repeated log messages are being reanalyzed and churned to disk.
Thankfully the Wazuh agent has a flood protection mechanism to prevent out of control log production on one system from creating disruptions to your network or to your Wazuh/Elastic services. In this lab we will create a small log flood and observe how it is gracefully contained by the Wazuh agent before it departs the system where the logs are produced. We will also take a look at the leaky bucket queue that Wazuh uses to accomplish this. Lastly we will note the alerts that are produced to keep us informed about the onset of, escalation of, and recovery from log flooding events.
Configure the Wazuh agent client buffer on linux-agent
- In this lab, we will limit agent log production to 20 events per second (eps). By default, this limit is prevented from being set to lower than 50, so we will override that by changing the relevant internal options setting. This does not actually set an eps limit. Rather, it is a strictly agent-side setting that protects the agent from being inadvertently subjected to overly restrictive eps limits pushed to it via Wazuh manager centralized configuration. Here we make it possible to enforce an eps as low as 10.
- #echo“agent.min_eps=10″ >> /var/ossec/etc/local_internal_options.conf
- Open /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf and find the <client_buffer> section, which looks like this:
- <client_buffer>
- <!– Agent buffer options –>
- <disabled>no</disabled>
- <queue_size>5000</queue_size>
- <events_per_second>500</events_per_second>
- </client_buffer>
- Restart the Wazuh agent
- #ossec-control restart
Note
The client buffer is explained in detail in the Wazuh User manual. Search for “Anti-flooding mechanism”. In brief, it allows a Wazuh agent to limit the rate at which it sends log events to the Wazuh Manager. If events are produced at a rate in excess of the configured eps limit, then they are stored in a leaky bucket queue until the eps rate slows down enough that the queue contents can be sent along to the Wazuh Manager. If the queue gets full, then any new events are droped, i.e the bucket leaks. Various alerts are sent to the Wazuh Manager about all of this.
- To ensure our flood simulation causes queueing and ultimately overflows the queue, change <queue_size> to 500 and <events_per_second> to 20. Save and close ossec.conf. The new section should look like this:
- <client_buffer>
- <!– Agent buffer options –>
- <disabled>no</disabled>
- <queue_size>500</queue_size>
- <events_per_second>20</events_per_second>
- </client_buffer>
Warning
These settings are small for simulation purposes. You would not want to make them this low in production.
Make Wazuh manager record alerts for each flooded event record
Because we will intentionally include the word “fatal” in the flooding log records we generate, they each will trigger generic Wazuh rule 1002 which has a low severity level of 2. By default, Wazuh Manager does not record alerts on rules of severity levels less than 3, so for this lab we will lower the threshold.
- Edit /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf and change <log_alert_level> from 3 to 1 so that the <alerts> section looks like below. Now alerts of all severity levels will show up in Kibana.
- <alerts>
- <log_alert_level>1</log_alert_level>
- <email_alert_level>12</email_alert_level>
- </alerts>
- Restart Wazuh Manager.
- #ossec-control restart
Generate a log flood on linux-agent
- Create a script called /usr/local/bin/makeflood, with this content:
- #!/bin/bash
- for i in {1..10000}
- do
- echo -n “1:floodtest:Feb 3 03:08:47 linux-agent centos: fatal firehose $i” | ncat –Uu /var/ossec/queue/ossec/queue
- echo -n “.”
- done
Note
While we could write records to a log file monitored by Wazuh agent, this script takes an even faster approach of writing records directly to the Wazuh agent’s internal socket where, for example, ossec-logcollector streams new log lines from log files. The script uses netcat to do this, but any tool that can write datagrams to a Unix socket will do the job. Sometimes it is desirable to have a script on a Wazuh agent send results directly back to the Wazuh manager while completely bypassing the agent’s filesystem. The quoted log line that is piped to netcat consists of three colon-separated parts. First, the “1” corresponds to the syslog log type. The second field causes the location metadata value to be set to “floodtest”. After that is a log line just like you might see in /var/log/messages.
- Make the script executable and then run it to generate a rapid flood of 10,000 log entries.
- #chmod700 /usr/local/bin/makeflood
- #makeflood
- Notice that the periods representing log messages are scrolling acrosss the screen at a rate well above our 20 eps limit.
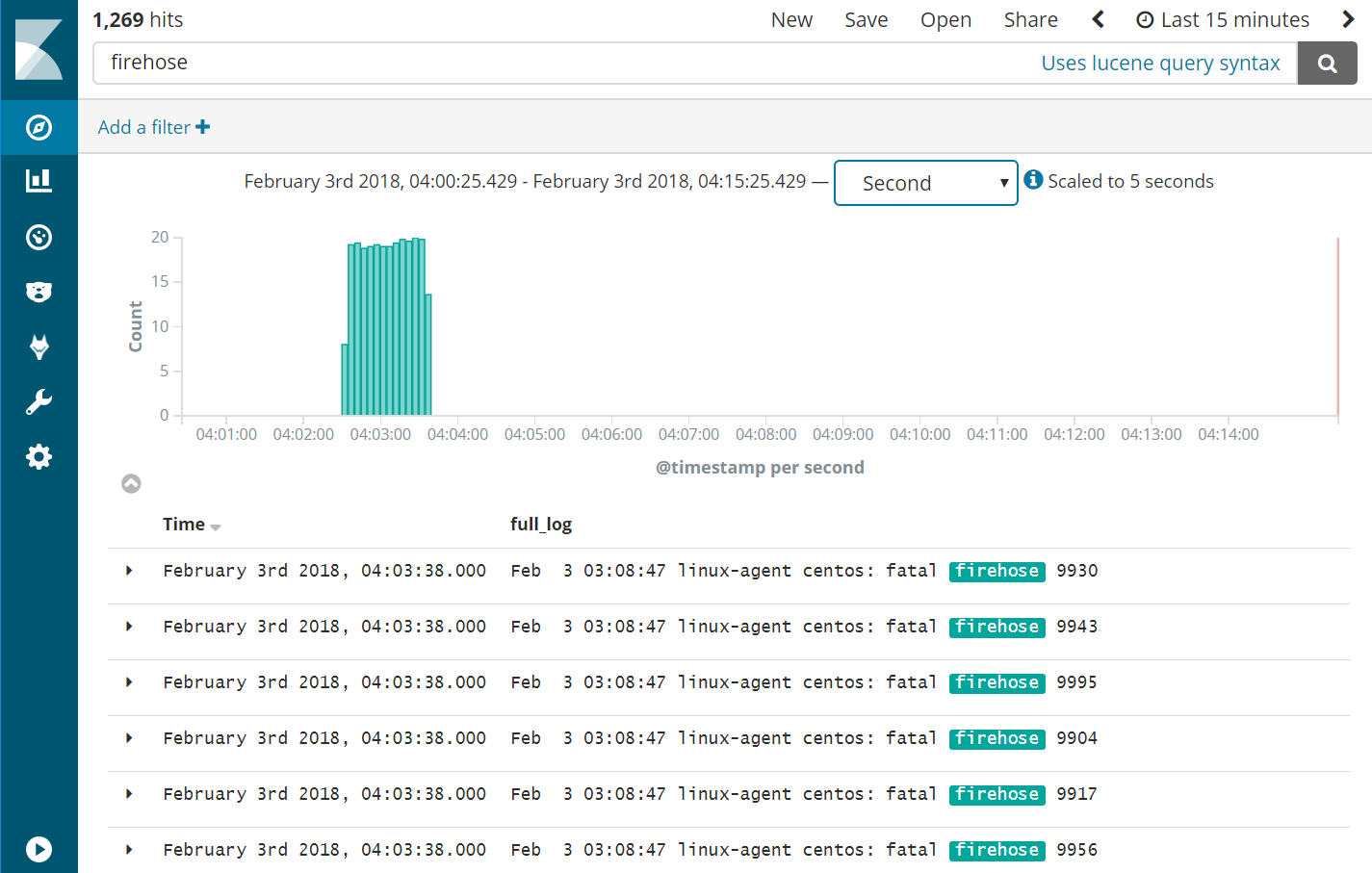
See what happened according to Kibana
- Query Kibana for “firehose”. Click [Add] next to “full_log” for readability. Change the scale from “Auto” to “Second”.
|
Wazuh Agent Client Buffer |
- Notice that the flooding events only arrived at the Wazuh Manager at a rate of 20 eps, our intended limit. The client buffer eps limit worked!
- Notice that only 1,269 hits are reported for a flood. It appears many of the flooded events were lost.
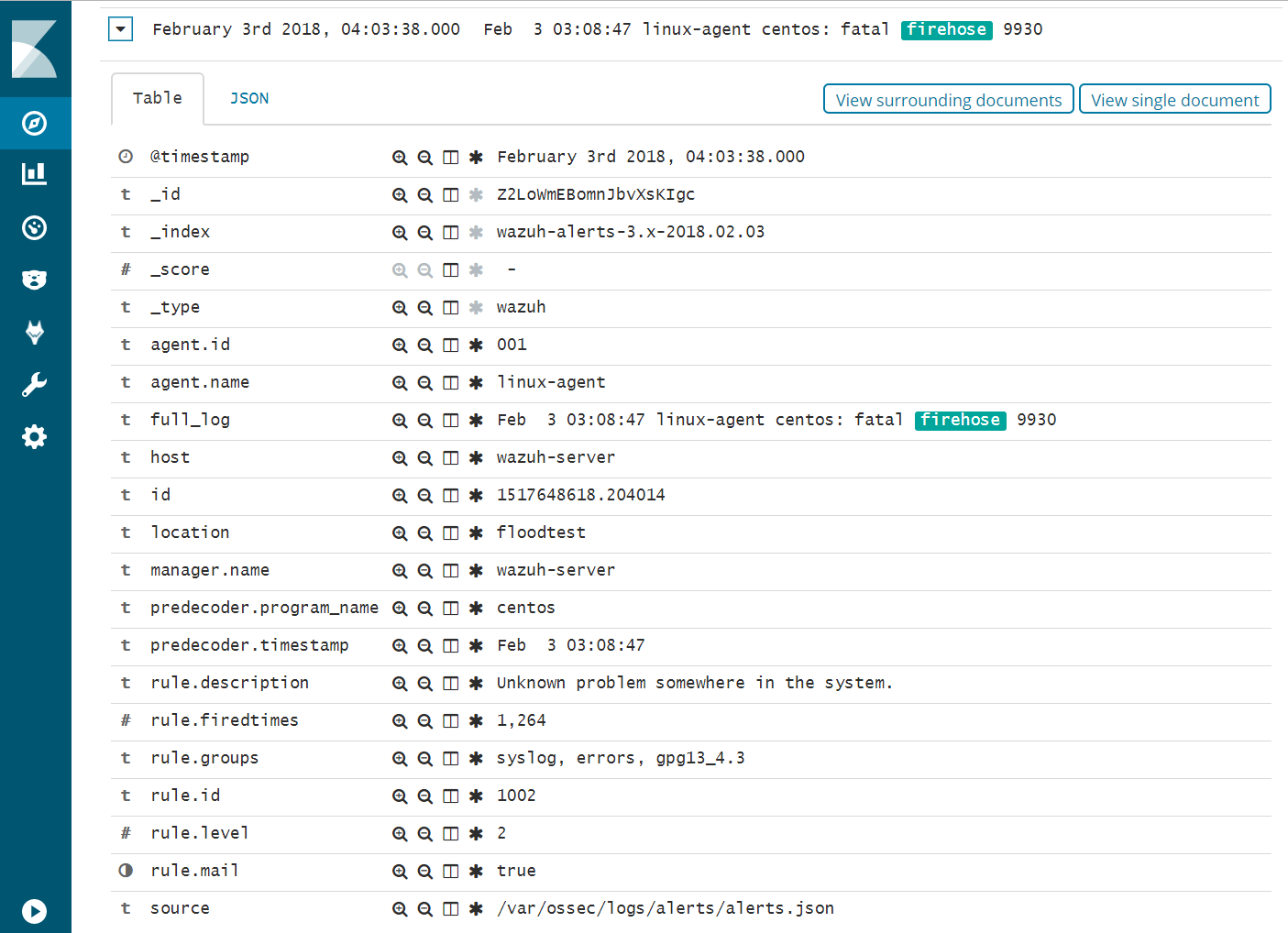
- Expand one of the “firehose” records and compare the field values to the script you used to produce these records.
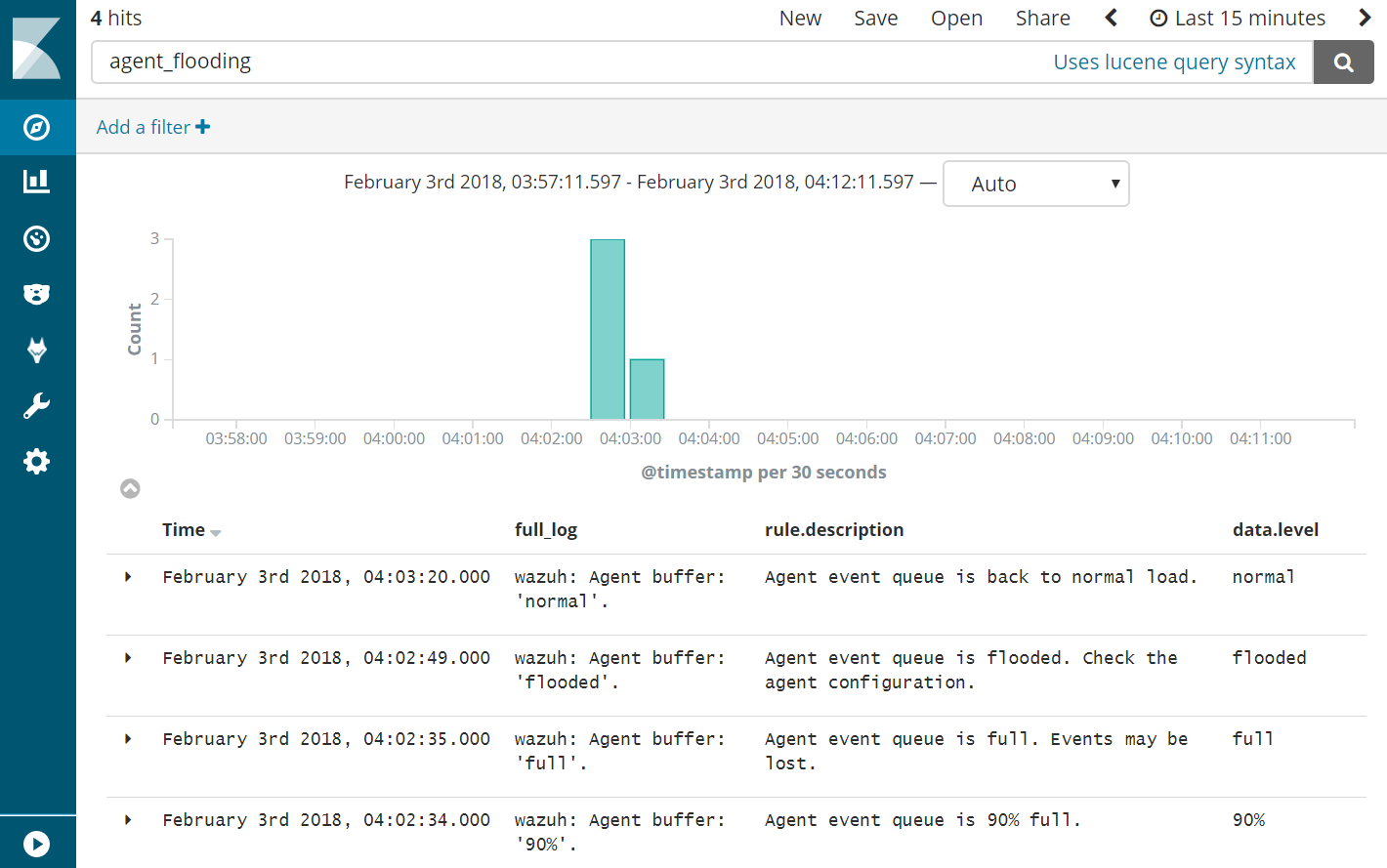
- Query Kibana for “agent_flooding”. Click [Add] additionally next to “rule.description” and “data.level” for readability.
- Observe how Wazuh alerts us at various stages of a flooding event so that we can know when we need to intervene with an over-logging system that is not recovering to a normal state on its own.
Return linux-agent to normal client buffer settings
- In the <client_buffer> section of /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf file, change it back to this:
- <client_buffer>
- <!– Agent buffer options –>
- <disabled>no</disabled>
- <queue_size>5000</queue_size>
- <events_per_second>500</events_per_second>
- </client_buffer>
- Restart the Wazuh agent
- #ossec-control restart
Congratulations on completing this lab. You survived the log flood!
How to update java on centos
First of all, check your current Java version with this command:
java -version
Example:
$ java -version
java version "1.8.0_181"
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment (build 1.8.0_181-b13)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM (build 25.181-b13, mixed mode)
If your installed version is not Java 8 update 181, then you could follow the step in order to download the latest Java version and install it:
- Download the Java JRE package for RPM-based distributions:
curl -Lo jre-8-linux-x64.rpm --header "Cookie: oraclelicense=accept-securebackup-cookie" "https://download.oracle.com/ otn-pub/java/jdk/8u181-b13/ "96a7b8442fe848ef90c96a2fad6ed6 d1/jre-8u181-linux-x64.rpm - Check that the package was successfully downloaded:
rpm -qlp jre-8-linux-x64.rpm > /dev/null 2>&1 && echo "Java package downloaded successfully" || echo "Java package did not download successfully" - Install the package using
yum:yum -y install jre-8-linux-x64.rpm rm -f jre-8-linux-x64.rpm
Wazuh-agent troubleshooting guide.
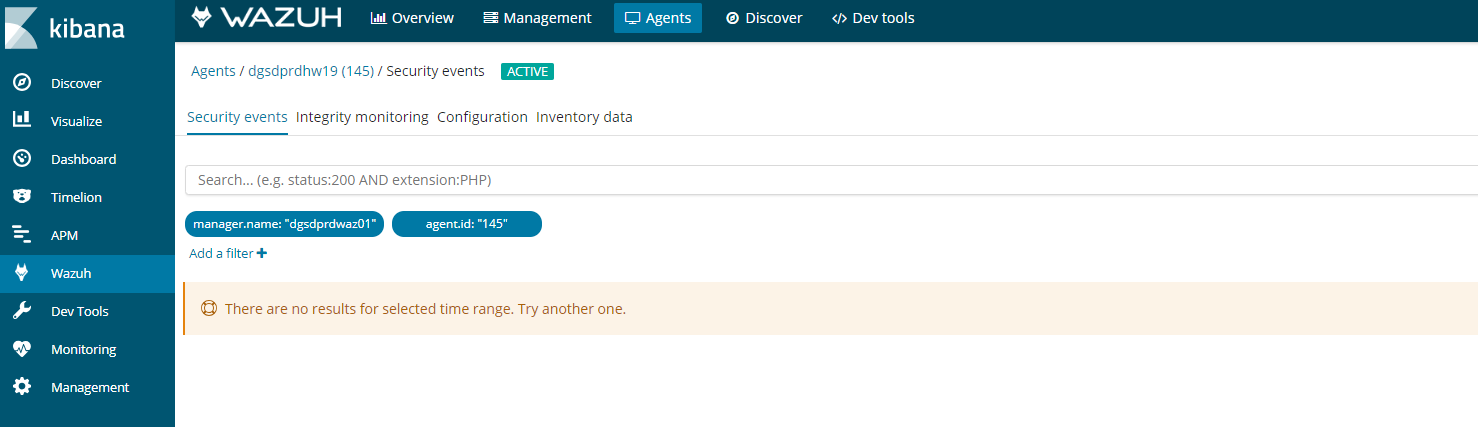
If you see this error in kibana on an agent. It could be for a number of reasons.
Follow this process to figure it out.
- Agent buffer on the client is full, which is caused by flood of alerts. The agents have a buffer size to keep resources on the clients consistent and minimal. If this fills up then kibana will stop collecting data.
- The first step is the easiest log into the client and restart the client by
- Systemctl restart wazuh-agent
- /etc/init.d/wazuh-agent restart
- And windows open the agent and click on restart
- If you go kibana
- Click on agents
- Then find your agent
- Click on a agent
- Click security audit
It should look something like this.
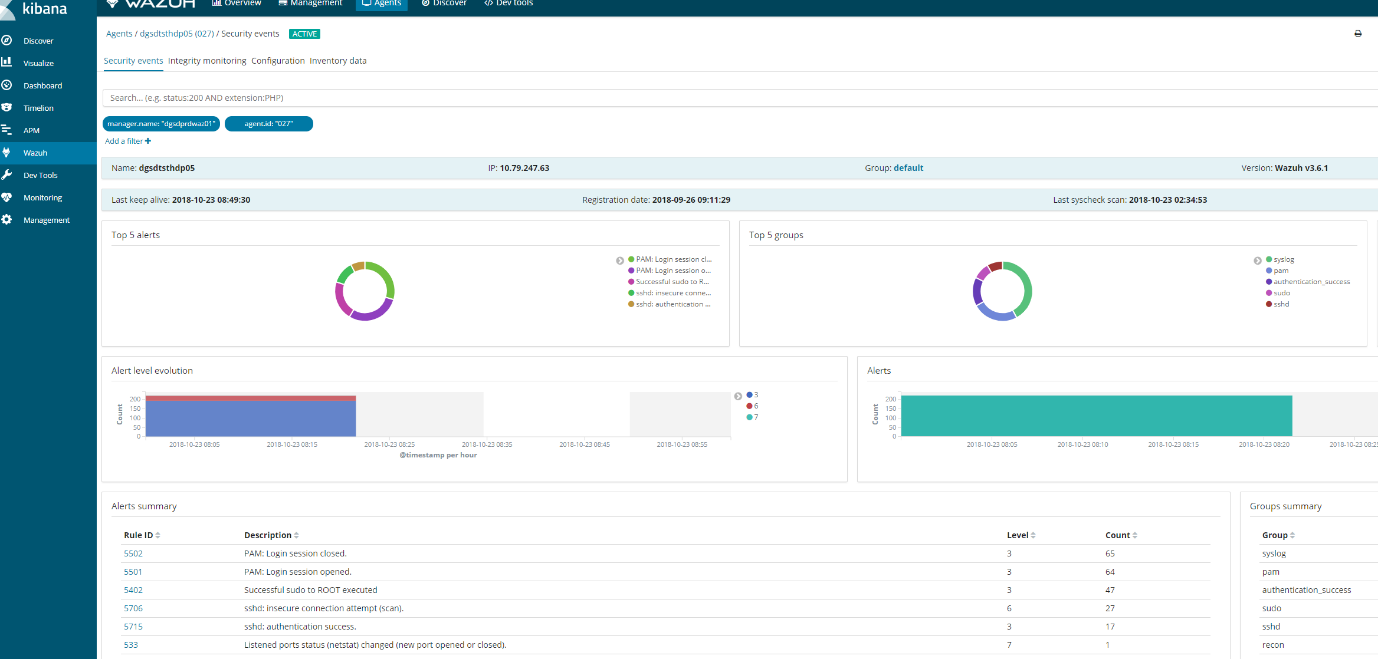
If this does not appear then we need to check wazuh-manager
Reason1 :Space issues
Logs can stop generating if elastic-search partition reaches 85% full and put the manager into read only mode.
# ls /usr/share/elasticsearch/data/ (lives on a different lvm)
# ls /var/ossec (lives on a different lvm)
-
- Ensure these partitions have plenty of space or wazuh will go into read only mode
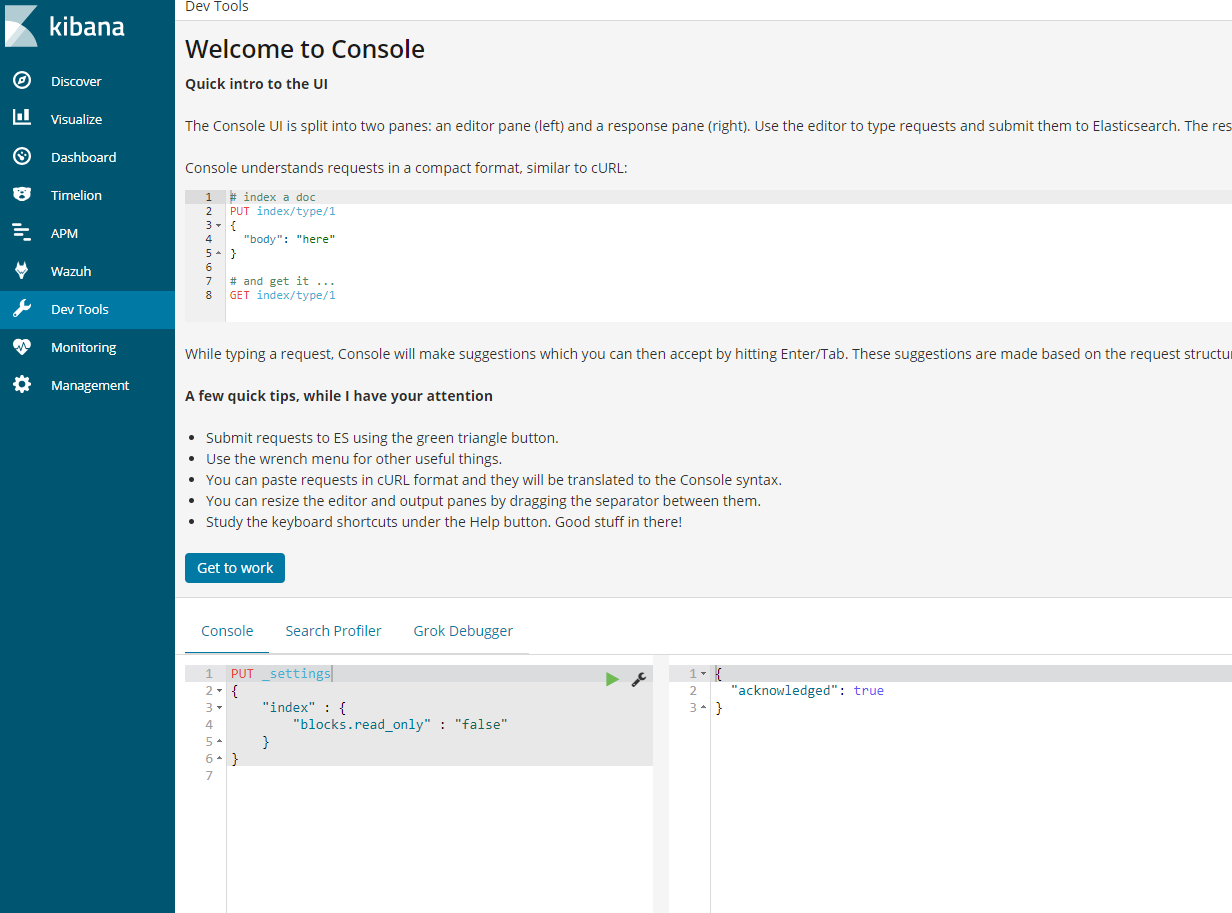
- Ones you have ensure there is adequate space you will need to execute a command in kibana to get it working again.
PUT _settings{ “index“ : { “blocks.read_only“ : “false” }}
-
- In kibana, go to dev tools and put the above code and play the code.
Alternative command that does the same thing.
- curl –XPUT ‘http://localhost:9200/_settings‘ –H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ –d‘ { “index”: { “blocks”: { “read_only_allow_delete“: “false” } } } ‘
- Next restart wazuh-manager and ossec
- /var/ossec/bin/ossec-control restart
- Systemctl restart wazuh-manager
Reason 2: Ensure services are running and check versions
- Elasticsearch:curl –XGET ‘localhost:9200’
[root@waz01~]# curl localhost:9200/_cluster/health?pretty
{
“cluster_name” : “elasticsearch“,
“status” : “yellow”,
“timed_out” : false,
“number_of_nodes” : 1,
“number_of_data_nodes” : 1,
“active_primary_shards” : 563,
“active_shards” : 563,
“relocating_shards” : 0,
“initializing_shards” : 0,
“unassigned_shards” : 547,
“delayed_unassigned_shards” : 0,
“number_of_pending_tasks” : 0,
“number_of_in_flight_fetch” : 0,
“task_max_waiting_in_queue_millis” : 0,
“active_shards_percent_as_number” : 50.72072072072073
}
- Kibana:/usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana –V
[root@waz01 ~]# /usr/share/kibana/bin/kibana -V
6.4.0Logstash:/usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash –V
[root@waz01 ~]# /usr/share/logstash/bin/logstash -V
logstash 6.4.2
-
- Check to see if wazuh-manager and logstash are running
- systemctl status wazuh–manager
Active and working
[root@waz01 ~]#systemctl status wazuh-manager
● wazuh-manager.service – Wazuh manager
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/wazuh-manager.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-10-18 12:25:53 BST; 4 days ago
Process: 4488 ExecStop=/usr/bin/env ${DIRECTORY}/bin/ossec-control stop (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
Process: 4617 ExecStart=/usr/bin/env ${DIRECTORY}/bin/ossec-control start (code=exited, status=0/SUCCESS)
CGroup: /system.slice/wazuh-manager.service
├─4635 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-authd
├─4639 /var/ossec/bin/wazuh-db
├─4656 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-execd
├─4662 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-analysisd
├─4666 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-syscheckd
├─4672 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-remoted
├─4675 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-logcollector
├─4695 /var/ossec/bin/ossec-monitord
└─4699 /var/ossec/bin/wazuh-modulesd
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started wazuh-db…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started ossec-execd…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started ossec-analysisd…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started ossec-syscheckd…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started ossec-remoted…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started ossec-logcollector…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started ossec-monitord…
Oct 18 12:25:51 waz01env[4617]: Started wazuh-modulesd…
Oct 18 12:25:53 waz01env[4617]: Completed.
Oct 18 12:25:53 waz01systemd[1]: Started Wazuh manager.
- systemctl status logstash
Active and working
[root@waz01~]#systemctl status logstash
● logstash.service – logstash
Loaded: loaded (/etc/systemd/system/logstash.service; enabled; vendor preset: disabled)
Active: active (running) since Mon 2018-10-15 23:44:21 BST; 1 weeks 0 days ago
Main PID: 11924 (java)
CGroup: /system.slice/logstash.service
└─11924 /bin/java -Xms1g -Xmx1g –XX:+UseParNewGC -XX:+UseConcMarkSweepGC –XX:CMSInitiatingOccupancyFraction=75 -XX:+UseCMSInitiatingOccupancyOnly –Djava.awt.headless=true –Dfile.encoding=UTF-8 –Djruby.compile.invokedynamic=true –Djruby.jit.threshold=0 -XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError –Djava.security.egd=file:/dev/urandom -cp /usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/jars/animal-sniffer-annotations-1.14.jar:/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/jars/commons-codec-1.11.jar:/u…
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,581][WARN ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Detected a 6.x and above cluster: the `type` event field won’t be used to determine the document _type {:es_version=>6}
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,604][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] New Elasticsearch output {:class=>”LogStash::Outputs::ElasticSearch“, :hosts=>[“//localhost:9200”]}
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,616][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Using mapping template from {:path=>nil}
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,641][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Attempting to install template {:manage_template=>{“template”=>”logstash-*”, “version”=>60001, “settings”=>{“index.refresh_interval“=>”5s”}, “mappings”=>{“_default_”=>{“dynamic_templates”=>[{“message_field”=>{“path_match”=>”mess
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,662][INFO ][logstash.filters.geoip ] Using geoip database {:path=>”/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/logstash-filter-geoip-5.0.3-java/vendor/GeoLite2-City.mmdb”}
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,925][INFO ][logstash.inputs.file ] No sincedb_path set, generating one based on the “path” setting {:sincedb_path=>”/var/lib/logstash/plugins/inputs/file/.sincedb_b6991da130c0919d87fbe36c3e98e363″, :path=>[“/var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json“]}
Oct 15 23:44:41 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:41,968][INFO ][logstash.pipeline ] Pipeline started successfully {:pipeline_id=>”main”, :thread=>”#<Thread:0x63e37301 sleep>”}
Oct 15 23:44:42 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:42,013][INFO ][logstash.agent ] Pipelines running {:count=>1, :running_pipelines=>[:main], :non_running_pipelines=>[]}
Oct 15 23:44:42 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:42,032][INFO ][filewatch.observingtail ] START, creating Discoverer, Watch with file and sincedb collections
Oct 15 23:44:42 waz01logstash[11924]: [2018-10-15T23:44:42,288][INFO ][logstash.agent ] Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
If any of these are failed restart them.
- systemctl restart logstashsystemctl restart elasticsearchsystemctl restart wazuh-manger
Reason 3: Logstash is broken
- Check the logs for errors.
- tail /var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log
Possible error#1 :
[root@waz01 ~]# tail /var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Retrying individual bulk actions that failed or were rejected by the previous bulk request. {:count=>1}
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] retrying failed action with response code: 403 ({“type”=>”cluster_block_exception“, “reason”=>”blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”})
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] retrying failed action with response code: 403 ({“type”=>”cluster_block_exception“, “reason”=>”blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”})
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Retrying individual bulk actions that failed or were rejected by the previous bulk request. {:count=>2}
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] retrying failed action with response code: 403 ({“type”=>”cluster_block_exception“, “reason”=>”blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”})
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Retrying individual bulk actions that failed or were rejected by the previous bulk request. {:count=>1}
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Retrying individual bulk actions that failed or were rejected by the previous bulk request. {:count=>2}
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,475][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Retrying individual bulk actions that failed or were rejected by the previous bulk request. {:count=>3}
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,476][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] retrying failed action with response code: 403 ({“type”=>”cluster_block_exception“, “reason”=>”blocked by: [FORBIDDEN/12/index read-only / allow delete (api)];”})
[2018-10-09T17:37:59,476][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Retrying individual bulk actions that failed or were rejected by the previous bulk request. {:count=>1}
Possible error#2 :
[2018-10-15T20:06:10,967][ERROR][org.logstash.Logstash ] java.lang.IllegalStateException: Logstash stopped processing because of an error: (SystemExit) exit
[2018-10-15T20:06:26,863][FATAL][logstash.runner ] An unexpected error occurred! {:error=>#<ArgumentError: Path “/var/lib/logstash/queue” must be a writable directory. It is not writable.>, :backtrace=>[“/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:447:in `validate'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:229:in `validate_value‘”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:140:in `block in validate_all‘”, “org/jruby/RubyHash.java:1343:in `each'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:139:in `validate_all‘”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/runner.rb:278:in `execute'”, “/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/clamp-0.6.5/lib/clamp/command.rb:67:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/runner.rb:237:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/clamp-0.6.5/lib/clamp/command.rb:132:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/lib/bootstrap/environment.rb:73:in `<main>'”]}
[2018-10-15T20:06:26,878][ERROR][org.logstash.Logstash ] java.lang.IllegalStateException: Logstash stopped processing because of an error: (SystemExit) exit
[2018-10-15T20:06:42,543][FATAL][logstash.runner ] An unexpected error occurred! {:error=>#<ArgumentError: Path “/var/lib/logstash/queue” must be a writable directory. It is not writable.>, :backtrace=>[“/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:447:in `validate'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:229:in `validate_value‘”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:140:in `block in validate_all‘”, “org/jruby/RubyHash.java:1343:in `each'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:139:in `validate_all‘”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/runner.rb:278:in `execute'”, “/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/clamp-0.6.5/lib/clamp/command.rb:67:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/runner.rb:237:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/clamp-0.6.5/lib/clamp/command.rb:132:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/lib/bootstrap/environment.rb:73:in `<main>'”]}
[2018-10-15T20:06:42,557][ERROR][org.logstash.Logstash ] java.lang.IllegalStateException: Logstash stopped processing because of an error: (SystemExit) exit
[2018-10-15T20:06:58,344][FATAL][logstash.runner ] An unexpected error occurred! {:error=>#<ArgumentError: Path “/var/lib/logstash/queue” must be a writable directory. It is not writable.>, :backtrace=>[“/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:447:in `validate'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:229:in `validate_value‘”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:140:in `block in validate_all‘”, “org/jruby/RubyHash.java:1343:in `each'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/settings.rb:139:in `validate_all‘”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/runner.rb:278:in `execute'”, “/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/clamp-0.6.5/lib/clamp/command.rb:67:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/logstash-core/lib/logstash/runner.rb:237:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/clamp-0.6.5/lib/clamp/command.rb:132:in `run'”, “/usr/share/logstash/lib/bootstrap/environment.rb:73:in `<main>'”]}
[2018-10-15T20:06:58,359][ERROR][org.logstash.Logstash ] java.lang.IllegalStateException: Logstash stopped processing because of an error: (SystemExit) exi
Probably need to reinstall logstash
1. Stop affected services:
# systemctl stop logstash# systemctl stop filebeat (this should not be installed on a stand alone setup as it causes performance issues.
2. Remove Filebeat
# yum remove filebeat
3. Setting up Logstash
# curl -so /etc/logstash/conf.d/01-wazuh.conf https://raw.githubusercontent.com/wazuh/wazuh/3.6/extensions/logstash/01-wazuh-local.conf# usermod -a -G osseclogstash
- Next step is to correct folder owner for certain Logstash directories:
# chown -R logstash:logstash /usr/share/logstash# chown -R logstash:logstash /var/lib/logstash
Note: if logstash still shows writing issues in the logs increase the permissions to
- chmod -R 766 /usr/share/logstash
- systemctl restart logstash
Now restart Logstash:
# systemctl restart logstash
5. Restart Logstash & run the curl command to ensure its not readonly.
- # systemctl restart logstash
- curl –XPUT ‘http://localhost:9200/_settings‘ –H ‘Content-Type: application/json’ –d‘ { “index”: { “blocks”: { “read_only_allow_delete“: “false” } } } ‘
- 6. Now check again your Logstash log file:
6. Now check again your Logstash log file:
# cat /var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log | grep –i -E “(error|warning|critical)”
Hopefully you see no errors being generated
Next check the plain log
- tail -10 /var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log
Good log output:
[root@waz01~]# tail -10 /var/log/logstash/logstash-plain.log
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,581][WARN ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Detected a 6.x and above cluster: the `type` event field won’t be used to determine the document _type {:es_version=>6}
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,604][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] New Elasticsearch output {:class=>”LogStash::Outputs::ElasticSearch“, :hosts=>[“//localhost:9200”]}
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,616][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Using mapping template from {:path=>nil}
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,641][INFO ][logstash.outputs.elasticsearch] Attempting to install template {:manage_template=>{“template”=>”logstash-*”, “version”=>60001, “settings”=>{“index.refresh_interval“=>”5s”}, “mappings”=>{“_default_”=>{“dynamic_templates”=>[{“message_field”=>{“path_match”=>”message”, “match_mapping_type“=>”string”, “mapping”=>{“type”=>”text”, “norms”=>false}}}, {“string_fields“=>{“match”=>”*”, “match_mapping_type“=>”string”, “mapping”=>{“type”=>”text”, “norms”=>false, “fields”=>{“keyword”=>{“type”=>”keyword”, “ignore_above“=>256}}}}}], “properties”=>{“@timestamp”=>{“type”=>”date”}, “@version”=>{“type”=>”keyword”}, “geoip“=>{“dynamic”=>true, “properties”=>{“ip“=>{“type”=>”ip“}, “location”=>{“type”=>”geo_point“}, “latitude”=>{“type”=>”half_float“}, “longitude”=>{“type”=>”half_float“}}}}}}}}
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,662][INFO ][logstash.filters.geoip ] Using geoip database {:path=>”/usr/share/logstash/vendor/bundle/jruby/2.3.0/gems/logstash-filter-geoip-5.0.3-java/vendor/GeoLite2-City.mmdb”}
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,925][INFO ][logstash.inputs.file ] No sincedb_path set, generating one based on the “path” setting {:sincedb_path=>”/var/lib/logstash/plugins/inputs/file/.sincedb_b6991da130c0919d87fbe36c3e98e363″, :path=>[“/var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json“]}
[2018-10-15T23:44:41,968][INFO ][logstash.pipeline ] Pipeline started successfully {:pipeline_id=>”main”, :thread=>”#<Thread:0x63e37301 sleep>”}
[2018-10-15T23:44:42,013][INFO ][logstash.agent ] Pipelines running {:count=>1, :running_pipelines=>[:main], :non_running_pipelines=>[]}
[2018-10-15T23:44:42,032][INFO ][filewatch.observingtail ] START, creating Discoverer, Watch with file and sincedb collections
[2018-10-15T23:44:42,288][INFO ][logstash.agent ] Successfully started Logstash API endpoint {:port=>9600}
Now that we have all clear, let’s check component by component:
1. Check last 10 alerts generated in your Wazuh manager. Also, check the field timestamp, we must take care about the timestamp.
tail –10 /var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json
2. If the Wazuh manager is generating alerts from your view (step 1), then let’s check if Logstash is reading our alerts. You should see two processes: java for Logstash and ossec-ana from Wazuh.
# lsof /var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json (ossec-ana & java should be running if not restart ossec)
[root@waz01~]#lsof /var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json
COMMAND PID USER FD TYPE DEVICE SIZE/OFF NODE NAME
ossec-ana 4662ossec 10w REG 253,3 2060995503 201341089 /var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json
java 11924 logstash 93r REG 253,3 2060995503 201341089 /var/ossec/logs/alerts/alerts.json
3. If Logstash is reading our alerts, let’s check if there is an Elasticsearch index for today (wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.16)):
curl localhost:9200/_cat/indices/wazuh–alerts–3.x-*
[root@waz01~]# curl localhost:9200/_cat/indices/wazuh-alerts-3.x-*
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.07 HLNDuMjHS1Ox3iLoSwFE7g 5 1 294 0 1000.8kb 1000.8kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.25 Eg1rvDXbSNSq5EqJAtSm_A 5 1 247998 0 87.7mb 87.7mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.05 HHRnxqjtTKimmW6FEUUfdw 5 1 143 0 679.6kb 679.6kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.08 MqIJtCNQR3aU3inuv-pxpw 5 1 183 0 748kb 748kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.15 GIx8fMXnQ3ukrSkKmjbViQ 5 1 171191 0 45.9mb 45.9mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.10 W3pw1hDwSp2QAtRm0hwoaQ 5 1 896799 0 662.6mb 662.6mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.15 rnC7kyXRQSCSXm6wVCiWOw 5 1 2628257 0 1.8gb 1.8gb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.02 nKEdjkFOQ9abitVi_dKF3g 5 1 727934 0 232.7mb 232.7mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.21 FY0mIXGQQHmCpYgRgOIJhg 5 1 203134 0 63.5mb 63.5mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.01 mvYSVDZJSfa-F_5dKIBwAg 5 1 402155 0 129.9mb 129.9mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.18 _2WiGz6fRXSNyDjy8qPefg 5 1 2787147 0 1.8gb 1.8gb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.19 ebb9Jrt1TT6Qm6df7VjZxg 5 1 201897 0 58.3mb 58.3mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.13 KPy8HfiyRyyPeeHpTGKJNg 5 1 52530 0 13.7mb 13.7mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.23 T7YJjWhgRMaYyCT-XC1f5w 5 1 1074081 0 742.6mb 742.6mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.03 bMW_brMeRkSDsJWL6agaWg 5 1 1321895 0 715mb 715mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.18 B1wJIN1SQKuSQbkoFsTmnA 5 1 187805 0 52.4mb 52.4mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.04 CvatsnVxTDKgtPzuSkebFQ 5 1 28 0 271.1kb 271.1kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.21 AWVQ7D8VS_S0DHiXvtNB1Q 5 1 2724453 0 1.8gb 1.8gb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.27 8wRF0XhXQnuVexAxLF6Y5w 5 1 233117 0 79.2mb 79.2mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.13 wM5hHYMCQsG5XCkIquE-QA 5 1 304830 0 222.4mb 222.4mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.12 1aB7pIcnTWqZPZkFagHnKA 5 1 73 0 516kb 516kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.29 BXyZe2eySkSlwutudcTzNA 5 1 222734 0 73.7mb 73.7mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.04 x8198rpWTxOVBgJ6eTjJJg 5 1 492044 0 364.9mb 364.9mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.23 ZQZE9KD1R1y6WypYVV5kfg 5 1 216141 0 73.7mb 73.7mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.22 60AsCkS-RGG0Z2kFGcrbxg 5 1 218077 0 74.2mb 74.2mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.12 WdiFnzu7QlaBetwzcsIFYQ 5 1 363029 0 237.7mb 237.7mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.24 Loa8kM7cSJOujjRzvYsVKw 5 1 286140 0 106.3mb 106.3mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.17 zK3MCinOSF2_3rNAJnuPCQ 5 1 174254 0 48.3mb 48.3mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.17 A4yCMv4YTuOQWelbb3XQtQ 5 1 2703251 0 1.8gb 1.8gb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.02 lt8xvq2ZRdOQGW7pSX5-wg 5 1 148 0 507kb 507kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.08.31 RP0_5r1aQdiMmQYeD0-3CQ 5 1 28 0 247.8kb 247.8kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.28 iZ2J4UMhR6y1eHH1JiiqLQ 5 1 232290 0 78.6mb 78.6mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.09 FRELA8dFSWy6aMd12ZFnqw 5 1 428 0 895.1kb 895.1kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.16 uwLNlaQ1Qnyp2V9jXJJHvA 5 1 171478 0 46.5mb 46.5mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.14 WQV3dpLeSdapmaKOewUh-Q 5 1 226964 0 154.9mb 154.9mb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.09.11 2Zc4Fg8lR6G64XuJLZbkBA 5 1 203 0 772.1kb 772.1kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.16 p2F-trx1R7mBXQUb4eY-Fg 5 1 2655690 0 1.8gb 1.8gb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.08.29 kAPHZSRpQqaMhoWgkiXupg 5 1 28 0 236.6kb 236.6kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.08.28 XmD43PlgTUWaH4DMvZMiqw 5 1 175 0 500.9kb 500.9kb
yellow open wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.19 O4QFPk1FS1urV2CGM2Ul4g 5 1 2718909 0 1.8gb 1.8gb
4. If Elasticsearch has an index for today (wazuh-alerts-3.x-2018.10.16), the problem is probably selected time range in Kibana. To discard any error related to this, please go to Kibana > Discover, and look for
alerts in that section of Kibana itself. If there are alerts from today in the Discover section.
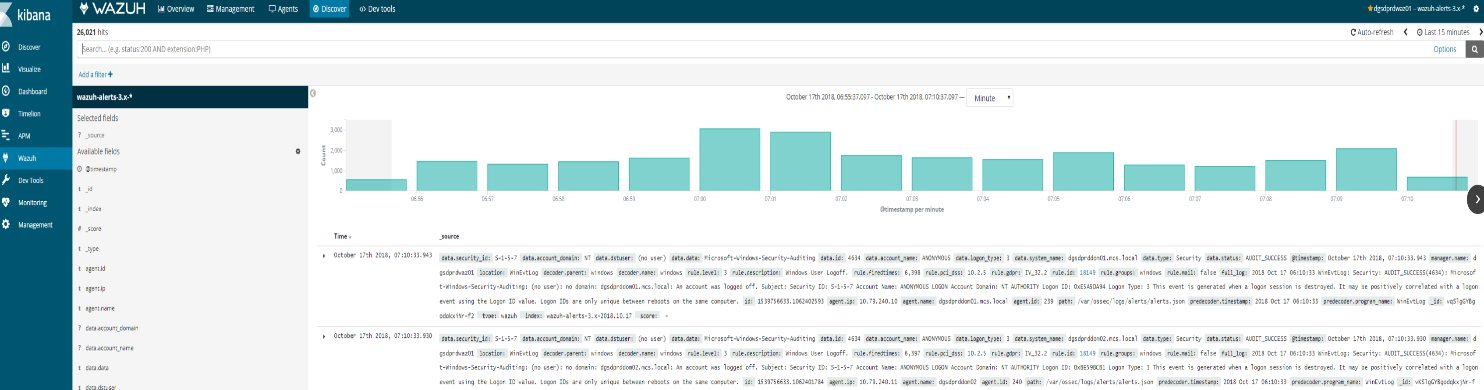
This means the Elasticsearch stack is finally working (at least at index level)
Reason 4: Agent buffer is full due to flood events. If this occurs events are not logged and data is lost. We want to drill down on a specific agent to figure out what is causing the issue.
Try to fetch data directly from Elasticsearch for the today’s index and for the agent 013. Copy and paste the next query in the Kibana dev tools:
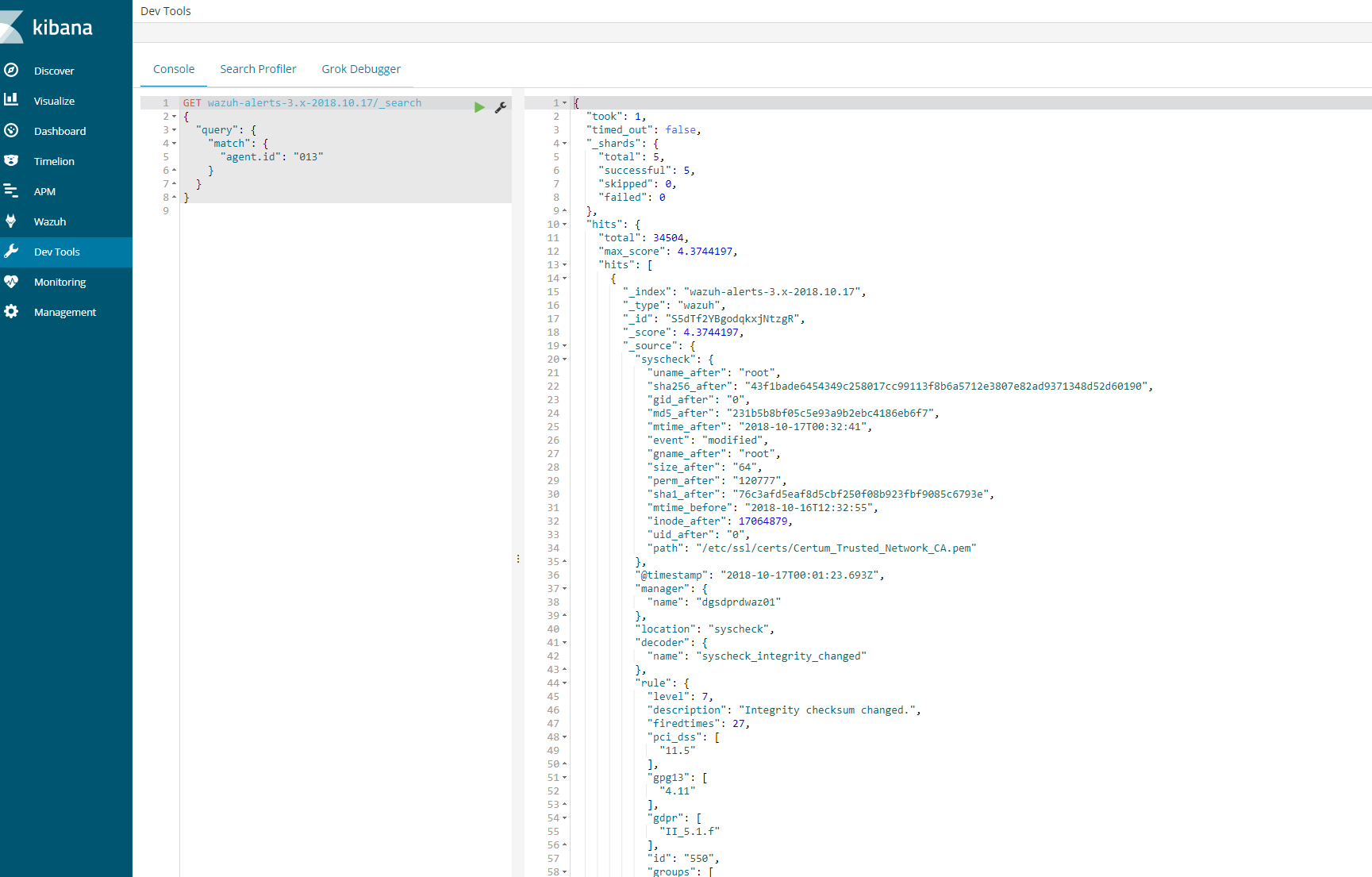
GET wazuh–alerts–3.x–2018.10.17/_search{ “query”: { “match”: { “agent.id“: “013” } }}
This should provide a log an output to show that the agent is logged in the indices for that day. If this is successful then we know that the logs are coming and kibana is able to communicate.
Next steps
- Login using SSH into the agent “013” and execute the next command:
wc –l /var/log/audit/audit.log cut –d‘/’ –f1 (centos)
wc –l /var/log/audit/syslog cut –d‘/’ f1(ubuntu)
- root@wazuh-03:/var/log# wc -l /var/log/syslog | cut -d’/’ -f1
- 36451
36451
Also, it would be nice if you provide us your audit rules, let’s check them using the next command:
# auditctl -l
It should show you a positive number, and that number is the number of lines in the audit.log file. Note down it.
- Now restart the Wazuh agent:
# systemctl restart wazuh-agent
We need to wait for syscheck scan is finished, this trick is useful to know exactly when it’s done:
# tail -f /var/ossec/logs/ossec.log | grep syscheck | grep Ending
The above command shouldn’t show anything until the scan is finished (it could take some time, be patient please). At the end, you should see a line like this:
2018/10/17 13:36:03 ossec–syscheckd: INFO: Ending syscheck scan (forwarding database).
Now, it’s time for checking the audit.log file again:
wc –l /var/log/audit/audit.log cut –d‘/’ –f1
wc –l /var/log/audit/syslog cut –d‘/’ f1
If you still see the agent buffer full after these steps then we need to do debugging.
tail -f /var/ossec/logs/ossec.log | grep syscheck | grep Ending
root@waz03:/var/log# cat /var/ossec/logs/ossec.log | grep –i -E “(error|warning|critical)”
2018/10/17 00:09:08 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer at 90 %.
2018/10/17 00:09:08 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer is full: Events may be lost.
2018/10/17 12:10:20 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer at 90 %.
2018/10/17 12:10:20 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer is full: Events may be lost.
2018/10/17 14:25:20 ossec-logcollector: ERROR: (1103): Could not open file ‘/var/log/messages’ due to [(2)-(No such file or directory)].
2018/10/17 14:25:20 ossec-logcollector: ERROR: (1103): Could not open file ‘/var/log/secure’ due to [(2)-(No such file or directory)].
2018/10/17 14:26:08 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer at 90 %.
2018/10/17 14:26:08 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer is full: Events may be lost.
2018/10/17 14:28:18 ossec-logcollector: ERROR: (1103): Could not open file ‘/var/log/messages’ due to [(2)-(No such file or directory)].
2018/10/17 14:28:18 ossec-logcollector: ERROR: (1103): Could not open file ‘/var/log/secure’ due to [(2)-(No such file or directory)].
2018/10/17 14:29:06 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer at 90 %.
2018/10/17 14:29:06 ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer is full: Events may be lost.
Debugging json alerts for specific agent 13
Ok, let’s debug your agent events using logall_json in the Wazuh manager instance.
Login using SSH into the Wazuh manager instance and edit the ossec.conf file.
- Edit the file /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf and look for the <global> section, then enable <logall_json>
<logall_json>yes</logall_json>
2. Restart the Wazuh manager
# systemctl restart wazuh-manager
3. Login using SSH into the Wazuhagent(13) instance, restart it and tail -f until it shows you the warning message:
# systemctl restart wazuh-agent# tail -f /var/ossec/logs/ossec.log | grep WARNING
4. Once you see ossec-agentd: WARNING: Agent buffer at 90 %. in the Wazuh agent logs,
then switch your CLI to the Wazuh manager instance again and
the next file we want to tail is from your Wazuh manager:
tail –f /var/ossec/logs/archives/archives.json
5. Now we can take a look into events in order to clarify what is flooding the agent “013”.
Once you have the log is seen, you can disable logall_json and restart the Wazuh manager.
6.
Log from tail –f /var/ossec/logs/archives/archives.json (wazuh-manager)
{“timestamp”:”2018-10-17T18:06:17.33+0100″,”rule”:{“level”:7,”description”:”Host-based anomaly detection event (rootcheck).”,”id”:”510″,”firedtimes”:3352,”mail”:false,”groups”:[“ossec”,”rootcheck”],”gdpr”:[“IV_35.7.d”]},”agent”:{“id”:”013″,”na
me”:”waz03“,”ip”:”10.79.244.143″},”manager”:{“name”:”waz01“},”id”:”1539795977.2752038221″,“full_log”:”File ‘/var/lib/kubelet/pods/2ff462ce-7233-11e8-8282-005056b518e6/containers/install-cni/e26aa5b1’ is owned by root and has written permissions to anyone.”,”decoder“:{“name”:”rootcheck“},”data”:{“title”:”File is owned by root and has written permissions to anyone.”,”file”:”/var/lib/kubelet/pods/2ff462ce-7233-11e8-8282-005056b518e6/containers/install-cni/e26aa5b1″},”location”:”rootcheck”}
{“timestamp”:”2018-10-17T18:06:17.35+0100″,”rule”:{“level”:7,”description”:”Host-based anomaly detection event (rootcheck).”,”id”:”510″,”firedtimes”:3353,”mail”:false,”groups”:[“ossec”,”rootcheck”],”gdpr”:[“IV_35.7.d”]},”agent”:{“id”:”013″,”name”:”waz03“,”ip”:”10.79.244.143″},”manager”:{“name”:”waz01“},”id”:”1539795977.2752038739″,”full_log”:”File ‘/var/lib/kubelet/pods/2ff462ce-7233-11e8-8282-005056b518e6/containers/install-cni/12cb9011’ is owned by root and has written permissions to anyone.”,”decoder“:{“name”:”rootcheck“},”data”:{“title”:”File is owned by root and has written permissions to anyone.”,”file”:”/var/lib/kubelet/pods/2ff462ce-7233-11e8-8282-005056b518e6/containers/install-cni/12cb9011″},”location”:”rootcheck”}
{“timestamp”:”2018-10-17T18:06:17.37+0100″,”rule”:{“level”:7,”description”:”Host-based anomaly detection event (rootcheck).”,”id”:”510″,”firedtimes”:3354,”mail”:false,”groups”:[“ossec”,”rootcheck”],”gdpr”:[“IV_35.7.d”]},”agent”:{“id”:”013″,”name”:”waz03“,”ip”:”10.79.244.143″},”manager”:{“name”:”waz01“},”id”:”1539795977.2752039257″,”full_log”:”File ‘/var/lib/kubelet/pods/2ff462ce-7233-11e8-8282-005056b518e6/containers/install-cni/4a930107’ is owned by root and has written permissions to anyone.”,”decoder“:{“name”:”rootcheck“},”data”:{“title”:”File is owned by root and has written permissions to anyone.”,”file”:”/var/lib/kubelet/pods/2ff462ce-7233-11e8-8282-005056b518e6/containers/install-cni/4a930107″},”location”:”rootcheck”}
{“timestamp”:”2018-10-17T18:06:17.40+0100″,”rule“:{“level”:7,”description”:”Host-based anomaly detection event
From the above log we can see that kubernetes is sending a lot of events to the agent causing the buffer to fill up. To solve this we particular issue from happening in future. We can disable this at the client level or the global level.
Here you can see the number of events from rootcheck in your archives.json:
cat archives.json grep rootcheck wc –l489
Here you can see the number of events from rootcheck and rule 510 in thearchives.json:
cat archives.json grep rootcheck grep 510 wc –l489
Here you can see the number of events from rootcheck and rule 510 and including “/var/lib/kubelet/pods/“ in your archives.json:
cat archives.json grep rootcheck grep 510 grep /var/lib/kubelet/pods/ wc –l489
So we have two options:
Option 1. Edit the ossec.conf from your Wazuh agent “013”. (This is the one I did)
– Login using SSH into the Wazuh agent “013” instance.
– Edit the file /var/ossec/etc/ossec.conf, and look for the rootcheck block, then put a <ignore> block for that directory.
<rootcheck>…<ignore>/var/lib/kubelet</ignore>…</rootcheck>
Restart the Wazuh agent “013”
# systemctl restart wazuh-agent
Option 2. Check in which group is your agent and edit its centralized configuration.
– Login using SSH into the Wazuh manager instance.
– Check the group where is agent “013”
# /var/ossec/bin/agent_groups -s –i 013
– Note down the group, example: default
– Edit the file under /var/ossec/etc/shared/default/agent.conf (replace default by the real group name, it could be different from my example),
then add the rootcheck ignore inside the <agent_config> block, example:
<agent_config> <!– Shared agent configuration here –> <rootcheck> <ignore>/var/lib/kuberlet</ignore> </rootcheck></agent_config>
– Restart the Wazuh manager
# systemctl restart wazuh-manager
– Restart the agent on client as well
# systemctl restart wazuh–agent
The solution #1 takes effect immediately.
The solution #2 will push the new configuration from the Wazuh manager to the Wazuh agent, once the agent receives it,
it auto restarts itself automatically and then it applies the new configuration. It could take a bit more time than solution #1.
On a side note, you can take a look at this useful link about the agent flooding:
The above link talks about how to prevent from being flooded.
Now the agent should show correctly in the 15min time range. If a bunch of client had the issue then you need to use ansible to send out a agent restart on all clients or setup a cron on all the machines to restart the agent every 24 hours.
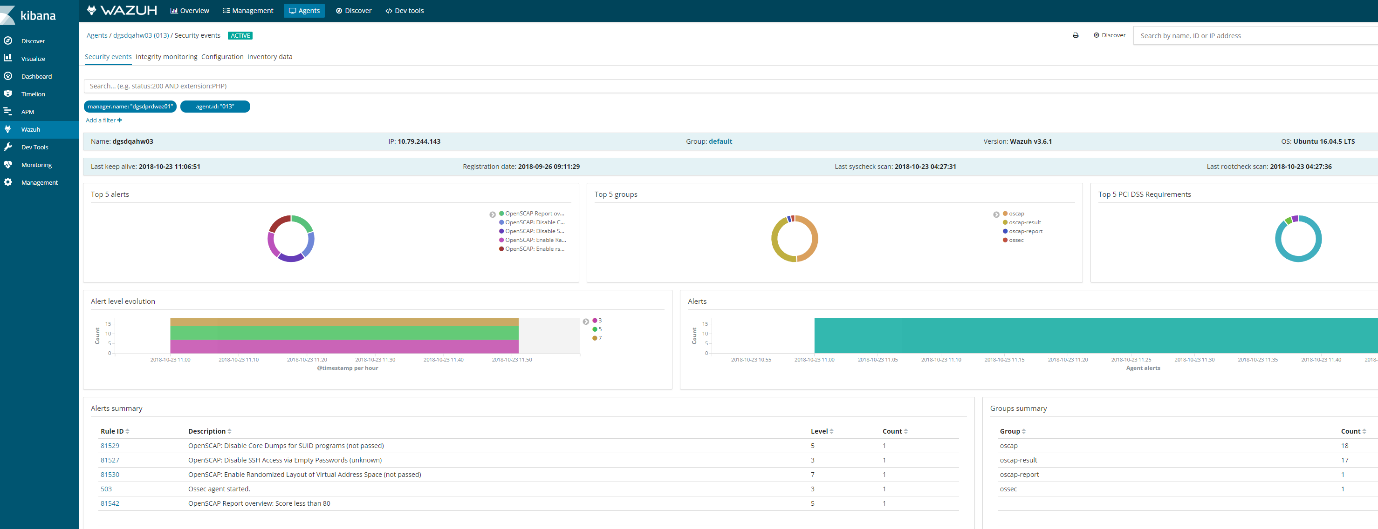
Discover on the agent should also show logs
Ansible adhoc command or playbook.
Example:
- ansible –i hosts–linuxdevelopment -a “sudo systemctl restart wazuh-agent” –vault-password-file /etc/ansible/vaultpw.txt -u ansible_nickt -k -K
How to diagnose a kernel panic caused by a killed process
You should install atop on your server as this is top on steroids and can help diagnose all kinds of server issues such as.
https://lwn.net/Articles/387202/ – Atop usage
- CPU load
- IO load
- Memory usage
- Process utilization of resources
- Paging/swaping
- etc…
- How you install atop on ubuntu/debian
- ‘apt-get install atop’
- Then you want to start the atop logging
- ‘/etc/init.d/atop start
- ‘/etc/init.d/atop start
Note : by default the atop logs every 10mins
Now lets say you console your VM or blade server. You see a message that states the server killed a process or ran out of memory or something.
Example:
- Out of memory: Kill process 11970 (php) score 80 or sacrifice child
Killed process 11970 (php) total-vm:1957108kB
When you reboot the server you will want to find out exactly how it happened. How you do this is by checking the kernel log. Now if you have kdump installed you can use that to get a dump of the kernel log and if not you can do this.
- dmesg | egrep -i ‘killed process’
- this will provide a log as indicated below
Kernel log
- [Wed July 10 13:27:30 2018] Out of memory: Kill process 11970 (php) score 80 or sacrifice child]
- [Wed July 10 13:27:30 2018] Killed process 11970 (php) total-vm:123412108kB, anon-rss:1213410764kB, file-rss:2420k]
Now once you have this log you can see the time stamp of when it occurred and you can use atop logs to drill down and find the process id, and see if you can see which daemon and or script caused the issue.
From the log ‘July 10 13:27:30 2018’ we can see the time stamp. Inside /var/log/atop you can do the following.
Run the following:
- ‘atop -r atop_20180710’
this will bring up a screen and you can toggle through the time intervals by using lowercase ‘T’ to move forward in time or Capital ‘T’ to go backward in time. - Once you find the time stamp you can
press – ‘c’ – full command-line per process to see which processes were running at that time stamp and you should be able to locate the id process from the kernel log
atop -r atop_20180710’
Example
- 3082 27% php
- 15338 27% php
- 26639 25% php
- 8520 8% php
- 8796 8% php
- 2157 8% /usr/sbin/apache2 -k start
- 11970 1% php – This is the process ID from the kernel log above and what appears to what was running. So we know it was a php script. Atop doesn’t always provide the exact script. However from the kernel log and this we can determine what was some type of rss feed. From this you can also see that it wasnt using very much CPU. This helps us determine that the php code is causing a memory leak and needs to be updated and or disabled.
- 10493 1% php
- 10942 1% php
- 5335 1% php
- 9964 0% php
Written by Nick Tailor
How to recover file system corruption on 4T LVM using DDrescue on a VM
How to recover file system corruption on 4T LVM on ubuntu using a VM
In this example we will be fixing a xfs filesystem that failed initial xfs_repair
If this happens don’t panic. We can fix most likely fix it.
Steps to do
Create new physical volume, volume group and logical volume
Now install ddrescue and make image of the corrupted file system on the new logical volume
Make swap size 30gigs – this is needed so when we repair the filesystem it doesn’t time out because it runs out of memory. Which tends to be the problem when trying to repair such large filesystems.
Sample outputs
Create rescue image on new logical volume
◦ ddrescue -d -r3 $oldfilesyetem imagefile.img loglocationpath.logfile
ddrescue -d -r3 /dev/recovery/data /mnt/recovery/recovery.img /mnt/recovery/recoverylog.logfile
Once the file is created we want to repair it using xfs_repair
– agno = 29
– agno = 9
– agno = 10
– agno = 11
– agno = 12
– agno = 13
– agno = 14
– 20:02:48: check for inodes claiming duplicate blocks – 88951488 of 88951488 inodes done
Phase 5 – rebuild AG headers and trees…
– 20:02:57: rebuild AG headers and trees – 41 of 41 allocation groups done
– reset superblock…
Phase 6 – check inode connectivity…
– resetting contents of realtime bitmap and summary inodes
– traversing filesystem …
– traversal finished …
– moving disconnected inodes to lost+found …
Phase 7 – verify and correct link counts…
Done
Written By Nick Tailor
How to add DNS entries from Linux to Windows DNS
If you already have a linux server that is already joined to the domain.
Its really simple to do, provided that you allow dynamic updates to your dns. If your server is not joined to the domain then please check out my how to add linux server to windows domain post.
Now if your deploying a server from a lab environment that isnt already joined to the domain, you can use this script to achieve it. Since you need DNS already created in windows DNS inorder to join a new server to your domain this helps automate that process.
What it will do is find the ip of the origin server, you can manually enter the hostname into the script or set it up as a argument to enter upon running the script. I just plug it in, and when its done running, it will have created the forward and reverse records for the new server by adding dns through a server that was already joined.
http://www.nicktailor.com/files/dnsaddwindowsscript (actual script)
#!/bin/sh
#This part will find the ip of the server
ADDR=`/sbin/ifconfig eth0 | grep ‘inet addr’ | awk ‘{print $2}’ | sed -e s/.*://`
#This part will provide the reverse arpa record based on the ip of the server grabbed from above.
rr=$(printf %s “$ADDR.” | tac -s.)in-addr.arpa
#This is just a hostname I plugged in because I was too lazy to have the server host itself. You can change this if you want.
HOST=`testnick.nicktailor.com`
#This portion of the script will connect to a server via ssh and run the dnsupdate through a server already joined to the domain, and add the records to the windows dns server.
ssh -qt SOMEHOST echo -e “server 192.168.1.10\nupdate add $HOST 600 A $ADDR\nsend\n” | nsupdate -v
ssh -qt SOMEHOST echo -e “server 192.168.1.10\nupdate add $rr 86400 PTR $HOST\nsend\n” | nsupdate -v
If all goes well you should be able to dig the results
dig any @nameserver testnick.nicktailor.com
Results:
; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 <<>> any @192.168.1.10 testnick.nicktailor.com
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 51960
;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;testnick.nicktailor.com. IN ANY
;; ANSWER SECTION:
testnick.nicktailor.com. 600 IN A 192.168.1.10
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 10.18.2.12#53(10.18.2.12)
;; WHEN: Fri Dec 2 13:51:13 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 61
dig any @nameserver 10.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa
Results:
; <<>> DiG 9.8.2rc1-RedHat-9.8.2-0.47.rc1.el6 <<>> any @10.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa
; (1 server found)
;; global options: +cmd
;; Got answer:
;; ->>HEADER<<- opcode: QUERY, status: NOERROR, id: 42354
;; flags: qr aa rd ra; QUERY: 1, ANSWER: 1, AUTHORITY: 0, ADDITIONAL: 0
;; QUESTION SECTION:
;10.1.168.192.in-addr.arpaa. IN ANY
;; ANSWER SECTION:
10.1.168.192.in-addr.arpa. 3600 IN PTR testnick.nicktailor.com.
;; Query time: 0 msec
;; SERVER: 10.18.2.12#53(10.18.2.12)
;; WHEN: Fri Dec 2 14:39:41 2016
;; MSG SIZE rcvd: 85
Written by Nick Tailor
How to automate your RedHat Satellite 5.x Channel Cloning
- In order for the scripts to work without sending your password to “ps” you will need to setup a config for spacecmd
Credential File
Spacecmd can be configured with a credentials file so you are not prompted for a username/password each time. This allows for easier scripting.
- Create a hidden spacecmd directory in your home. Lock down permissions.
mkdir ~/.spacecmd chmod 700 ~/.spacecmd
- Create a config file in the directory and give proper permissions.
touch ~/.spacecmd/config chmod 600 ~/.spacecmd/config
- Edit the config file and fill in the header, Spacewalk server fqdn, username, and password.
vim ~/.spacecmd/config [spacecmd] server=spacewalk.nicktailor.com username=usernamehere password=passwordhere
Clone scripts
http://www.nicktailor.com/files/clonechannel.redhat7.sh
http://www.nicktailor.com/files/clonechannel.redhat6.sh
http://www.nicktailor.com/files/clonechannel.redhat5.sh
REDHAT 7 (EXAMPLE)
#!/bin/bash
spacewalkServer=spacewalk.nicktailor.com
defaultOrgAdmin=USER
read -p “Enter to Continue”
How to RDP to VNC and authenticate using AD (Redhat 6)
For this we will be setting up VNC server and XRDP which allow you to use windows remote desktop terminal services client to connect to your linux desktop as you would any windows machine with centralized authentication using Active directory.
XRDP is a wonderful Remote Desktop protocol application that allows you to RDP to your servers/workstations from any Windows machine, MAC running an RDP app or even Linux using an RDP app such as Remmina. This was written for the new CentOS 6.5 on 64-bit but should work the same on any 6.x and 5.x Red Hat clone with the correct EPEL repositories.
Virtual Network Computing (VNC) is a graphical desktop sharing system that uses the Remote Frame Buffer protocol (RFB) to remotely control another computer. Essentially the Linux version of windows RDP.
We are going to make them work together so you can RDP from your windows machine to you linux desktop as you would any other windows machine using a windows RDP service. It create an ssh tunnel inside the RDP protocol to get to the vnc server and then authenicate against the active directory domain controller so you dont need to create users individually for vncserver.
First we need to download and install the EPEL repository for your correct version if you do now know what architecture you are using you can verify it with the below command. If the end shows x86_64 then you have a 64-bit install, if it shows i386 then it is a 32-bit install:
|
1
2
|
[root@server ~]# uname -r2.6.32-431.el6.x86_64 |
Once you determine your architecture then you can install the correct EPEL repository with the below commands:
|
1
2
|
wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/i386/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpmrpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm |
|
1
2
|
wget http://download.fedoraproject.org/pub/epel/6/x86_64/epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpmrpm -ivh epel-release-6-8.noarch.rpm |
You can verify that the EPEL repository is there by running the below command and you should see the EPEL repository listed as you can see here in line #10 which is highlighted:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
[root@server ~]# yum repolistLoaded plugins: fastestmirror, refresh-packagekit, securityLoading mirror speeds from cached hostfile * base: mirror.thelinuxfix.com * epel: mirror.cogentco.com * extras: centos.mirror.nac.net * updates: centos.mirror.netriplex.comrepo id repo name statusbase CentOS-6 - Base 6,367epel Extra Packages for Enterprise Linux 6 - x86_64 10,220extras CentOS-6 - Extras 14updates CentOS-6 - Updates 286repolist: 16,887 |
Once you have verified the EPEL repository is installed correctly you need to perform the last few steps below this will install XRDP and Tiger VNC Server for you to connect to. The Front end of XRDP uses the RDP protocol and internally it uses VNC to connect and display the Remote Desktop to you.
|
1
2
3
4
5
|
[root@server ~]# yum install xrdp tigervnc-server[root@server ~]# service vncserver start[root@server ~]# service xrdp start[root@server ~]# chkconfig xrdp on[root@server ~]# chkconfig vncserver on |
- If your vncserver did not start..probably due the /etc/sysconfig/vncserver file. You need at least one user and password configured.
- edit the file /etc/sysconfig/vncserver
- add the following below; adjust the users accordingly and save
VNCSERVERARGS[2]=”-geometry 800×600 -nolisten tcp -localhost”
- Now you su to your the user you created
- su ntailora
- then run vncpasswd
- type a complex password twice
- exit back to root by typing exit
- restart vncserver /etc/init.d/vncserver restart
Now to make it so that xrdp will authenticate against AD when creating a ssh tunnel through the rdp protocol.
NOTE: YOU WILL OF HAVE HAD TO FOLLOW MY EARLIER BLOG POST ON “HOW TO ADD A REDHAT SERVER TO ACTIVE DIRECTORY” FOR THIS PORTION TO WORK.
- we just need edit the pam authentication file that was created when xrdp was installed
- /etc/pam.d/xrdp-sesman
auth include password-auth
account include password-auth
session include password-auth
- Make a back up of the file /etc/pam.d/xrdp-sesman
- cp /etc/pam.d/xrdp-sesman /etc/pam.d/xrdp-sesman.bak
- Now copy your system-auth file over the /etc/pam.d/xrdp-sesman
- cp /etc/pam.d/system-auth /etc/pam.d/xrdp-sesman
It should look something like below. Iv bolded the sections that show the sssd authentication section in the file. Now you should be able to use your Active Directory(AD) credentials to authentication when trying to rdp to your linux desktop.
===================================================
#%PAM-1.0
# This file is auto-generated.
# User changes will be destroyed the next time authconfig is run.
auth required pam_env.so
auth sufficient pam_fprintd.so
auth sufficient pam_unix.so nullok try_first_pass
auth requisite pam_succeed_if.so uid >= 500 quiet
auth sufficient pam_sss.so use_first_pass
auth required pam_deny.so
account required pam_unix.so
account sufficient pam_localuser.so
account sufficient pam_succeed_if.so uid < 500 quiet
account [default=bad success=ok user_unknown=ignore] pam_sss.so
account required pam_permit.so
password requisite pam_cracklib.so try_first_pass retry=3
password sufficient pam_unix.so md5 shadow nullok try_first_pass use_authtok
password sufficient pam_sss.so use_authtok
password required pam_deny.so
session optional pam_keyinit.so revoke
session required pam_limits.so
session optional pam_oddjob_mkhomedir.so skel=/etc/skel
session [success=1 default=ignore] pam_succeed_if.so service in crond quiet use_uid
session required pam_unix.so
session optional pam_sss.so
============================================================
Cheers
If you have any questions email nick@nicktailor.com